
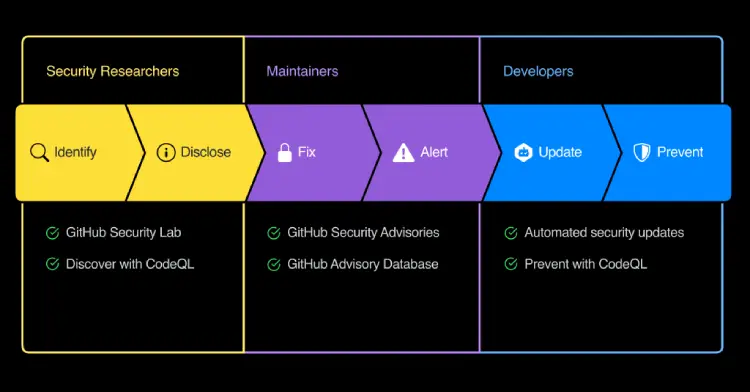
GitHub recently unveiled its work on GitHub Security Lab a space for security researchers and developers to fix vulnerabilities and share expertise in order to improve the overall security of GitHub’s code sharing ecosystem.
GitHub is performing strongly for Microsoft who acquired it for £5.6 billion last year as the software development and code repository is now used by 40 million developers. Unfortunately threat actors are also using the platform to host malware and in some case store stolen data, as happened in the Capital One breach.
The GitHub Security Lab will help security teams identify and report vulnerabilities in open source software. The security lab aims to make it easier for developers to use GitHub to fix bugs and patch projects.
Jamie Cool VP of product management security at GitHub commented in a security blog that: “GitHub Security Lab’s mission is to inspire and enable the global security research community to secure the world’s code. Our team will lead by example, dedicating full-time resources to finding and reporting vulnerabilities in critical open source projects. The team has already had over 100 CVEs issued for security vulnerabilities it has found.”
The GitHub Security lab is attempting to establish a cross industry community and so far is citing ‘time and expertise’ commitments from F5, Google, HackerOne, Intel, IOActive, J.P. Morgan, LinkedIn, Microsoft, Mozilla, NCC Group, Oracle, Trail of Bits, Uber and VMWare.
GitHub Security Lab
According to GitHub research when it comes to open source vulnerabilities 40 percent of them don’t have a CVE identifier and 70 percent of the issues discovered are still unpatched 30 days after developers have been alerted. The Security Lab aims to address this by bringing developers together to ensure that vulnerabilities are only disclosed when those responsible for fixing it are ready.
Importantly two months ago GitHub became a CVE Numbering Authority allowing it to issue CVE numbers when needed.
As part of this initiative GitHub has created a Security Advisories function that allows maintainers to work with: “Security researchers on security fixes in a private space, apply for a CVE directly from GitHub, and specify structured details about the vulnerability. Then, when they’re ready to publish the Security Advisory, GitHub will send security alerts to affected projects.”
In order to give developers the ability to move quickly GitHub have brought its automated security updates feature out of beta and made it generally available. This function pushes out notifications about vulnerabilities and importantly includes a pull request that can ‘update a vulnerable dependency to a fixed version.’
GitHub have also released a token scanning application which is run by the security lab that: “Within seconds of a commit being pushed to GitHub (or a repositories being made public), we scan it for token formats from 20 different cloud providers. When we detect a match, we notify the appropriate service provider and they take action, generally revoking the tokens and notifying the affected users.”
GitHub is making all data created by maintainers available for free in a GitHub Advisory Database.






